Coaxial cables
Coaxial cables description
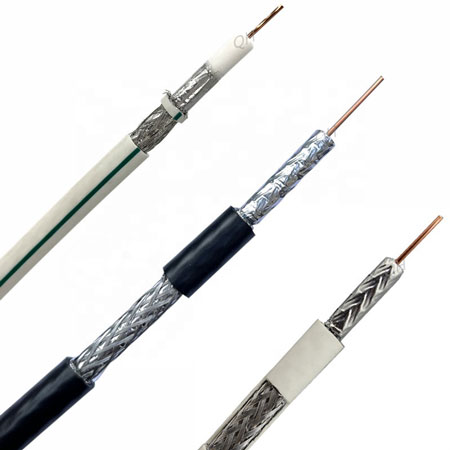
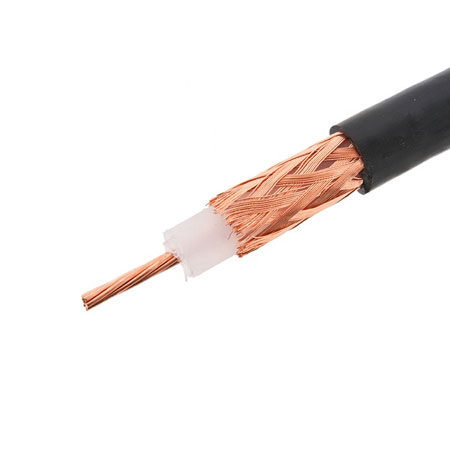
Coaxial cable is a high-performance signal transmission line featuring a four-layer structure: a central copper conductor, insulating dielectric, metallic shielding (usually copper or alloy mesh), and an outer insulating jacket. Designed for both analog and digital signal transmission, it offers superior shielding, low high-frequency loss, and broad bandwidth capability. Coaxial cable is widely used in applications such as cable TV, long-distance telephony, computer interconnects, LANs, and particularly in CCTV systems, where it ensures stable, high-quality video signal delivery from cameras to monitors. With excellent electrical performance and mechanical strength—including flexibility, tensile durability, and abrasion resistance—coaxial cable provides reliable, interference-resistant connectivity in demanding environments. Selecting the right coaxial cable depends on electrical, mechanical, and environmental requirements.
The growth of wireless and high-speed data applications has lead to the use of coaxial cables surpassing traditional video and telecommunications cables. With the development and standardization of coaxial cables used in various applications, coaxial cables have become common equipment in homes, offices, telecommunications facilities, railways, industrial plants, and government/public safety facilities. The diversification of such applications has led to the diversification of the types, grades and manufacturers of coaxial cables
The two main impedance used in coaxial cables are 75 ohms and 50 ohms. Unless there is visible identification content, it is impossible to determine the impedance of a coaxial cable from the outside. If the two impedance are confused, it is possible to cause damage to the device connector or the device itself, or at least to degrade the system performance. Although sometimes cross-used, 75 ohm cables are commonly used for video applications, while 50 ohm cables are more commonly used for data and wireless purposes. The type of device and device that needs to be connected determines the cable impedance that needs to be used.
- Cable performance depends on frequency
- Different cables have different power ratings,
- Different coaxial cables have the different shielding properties